A complete, radiant smile is a vital part of our overall appearance and confidence. However, missing teeth can impact not only our smile but also our oral health and self-assurance. Dental bridges provide a popular and effective solution to replace missing teeth and restore both aesthetics and functionality. In this blog post, we’ll explore what dental bridges are, their types, the benefits they offer, the procedure involved, aftercare tips, and who can benefit from this transformative dental treatment.
[ez-toc]
Also Read: Dental Implants: A Comprehensive Guide to a Lasting Smile
Understanding Dental Bridges
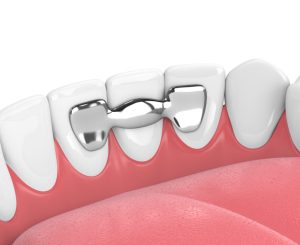
What is a Dental Bridge? A dental bridge is a fixed prosthetic device used to replace missing teeth by bridging the gap between natural teeth or dental implants. It consists of one or more artificial teeth (pontics) held in place by dental crowns or abutments attached to adjacent natural teeth or implants.
Types of Dental Bridges:
- Traditional Bridge: The most common type, where pontics are held in place by dental crowns on adjacent natural teeth.
- Cantilever Bridge: Used when adjacent teeth are present only on one side of the missing tooth/teeth.
- Maryland Bridge (Resin-Bonded Bridge): Metal or porcelain wings are bonded to the backs of adjacent teeth, providing support for the pontic.
The Benefits of Dental Bridges
- Restored Smile and Appearance:
- Dental bridges fill gaps caused by missing teeth, restoring a complete smile and enhancing facial aesthetics.
- Improved Speech and Chewing:
- Bridges restore proper speech and chewing functionality, making it easier to eat and speak without any hindrance.
- Prevent Teeth Shifting:
- Bridges prevent surrounding teeth from shifting into the gaps left by missing teeth, maintaining dental alignment.
- Preserve Facial Shape:
- By replacing missing teeth, dental bridges help preserve facial shape and prevent a sunken or aged appearance.
- Distribute Bite Forces:
- Bridges distribute bite forces evenly across the replaced teeth, preventing excessive pressure on adjacent natural teeth.
The Dental Bridge Procedure
1. Consultation and Planning:
- Your dentist will conduct a thorough examination, discuss your medical history, and formulate a personalized treatment plan based on your needs.
2. Preparation:
- The adjacent teeth or implants that will support the bridge are prepared by removing a portion of enamel to accommodate the crowns.
3. Impressions:
- Detailed impressions of the prepared teeth are taken to create an accurate model for constructing the bridge and crowns.
4. Temporary Bridge:
- A temporary bridge is placed to protect the exposed teeth while the permanent bridge is being fabricated.
5. Permanent Bridge Placement:
- Once the permanent bridge is ready, it is securely placed and adjusted for proper fit and bite.
Aftercare Tips for Dental Bridges
- Oral Hygiene:
- Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing, flossing, and using an antiseptic mouthwash to prevent gum disease and decay around the bridge.
- Regular Dental Check-ups:
- Visit your dentist for routine check-ups and cleanings to monitor the condition of the bridge and ensure its longevity.
- Balanced Diet:
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet to support overall oral health and prevent any damage to the bridge.
Also Read: Dental Health: Your Path to a Beautiful Smile
Who Can Benefit from Dental Bridges?
Dental bridges are an excellent option for individuals who:
- Have one or more missing teeth and wish to restore their smile and oral functionality.
- Are looking for a non-removable solution to replace missing teeth.
- Want to avoid more complex surgical procedures involved in dental implants.
How Long Does a Dental Bridge Last
The lifespan of a dental bridge can vary based on several factors, including the type of bridge, oral hygiene, diet, overall health, and habits of the individual. On average, a dental bridge can last anywhere from 5 to 15 years or more.
Here are some key factors that influence the longevity of a dental bridge:
Type of Bridge:
Traditional bridges (supported by natural teeth) or implant-supported bridges (anchored to dental implants) have different lifespans. Implant-supported bridges tend to last longer as they integrate with the jawbone, providing stability and durability.
Oral Hygiene:
Good oral hygiene is essential to maintain the health of the supporting teeth and gums. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups help prevent decay, gum disease, and other issues that could affect the bridge’s lifespan.
Diet and Habits:
Avoiding hard or sticky foods that could potentially damage or dislodge the bridge is important. Additionally, habits like teeth grinding (bruxism) can significantly reduce the lifespan of a bridge.
Material Quality:
The quality of materials used in the bridge, including the crowns and supporting framework, can impact its durability. High-quality materials tend to last longer.
Location of the Bridge:
Bridges in the front of the mouth generally experience less force and wear than those in the back. Front bridges may last longer due to reduced stress during biting and chewing.
Bone and Gum Health:
The health and density of the jawbone and gums can affect the stability and longevity of the dental implants if the bridge is implant-supported.
Regular Check-ups:
Regular dental check-ups allow the dentist to monitor the condition of the bridge and address any issues early, potentially extending its lifespan.
If a dental bridge becomes worn, damaged, or loose, it’s important to seek prompt dental care for repair or replacement. Your dentist will assess the condition of the bridge during routine check-ups and recommend any necessary actions to maintain its function and longevity.
It’s advisable to discuss the expected lifespan of your specific dental bridge with your dentist, as they can provide personalized insights based on your oral health and the type of bridge you have.
Can a Dental Bridge Be Removed and Recemented
Yes, a dental bridge can be removed and recemented under certain circumstances. The process of removing and recementing a dental bridge is typically performed by a dentist and involves careful handling and evaluation.
Here are common scenarios where a dental bridge might need to be removed and recemented:
Bridge Loosening:
If a dental bridge becomes loose due to issues like decay in the supporting tooth or changes in the structure of the supporting teeth, it may need to be removed and recemented.
Dental Hygiene Maintenance:
Routine maintenance and cleaning may necessitate temporarily removing the bridge to ensure proper oral hygiene in the area beneath the bridge.
Replacement of Dental Cement:
Over time, the dental cement holding the bridge in place may degrade or weaken. In such cases, the bridge can be removed, and new cement can be applied for a secure fit.
Assessment or Repair:
Dentists may need to remove and recement a bridge for assessment, repair, or modification to ensure it fits well and functions optimally.
Conclusion
Dental bridges offer a reliable and aesthetically pleasing way to replace missing teeth, restore your smile, and regain oral functionality. If you’re considering a dental bridge as a solution for missing teeth, consult with your dentist to explore the benefits and find the best option for your needs. Embrace the opportunity to bridge the gap in your smile and enhance your overall quality of life with a dental bridge. Smile confidently with a complete and beautiful smile!