What Are Bed bugs?
Bed bugs, scientifically known as Cimex lectularius, are small, parasitic insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals.
While they are not known to transmit diseases, their presence can cause discomfort, irritation, and affect your overall well-being. In this blog post, we’ll delve into understanding bed bug infestations, prevention measures, and remedies to deal with these unwelcome pests.
Also Read: Bed Bug Bites – All You Need to Know
[ez-toc]
What Do Bed Bugs Look Like?
Bedbugs are typically small and flat in shape, with a reddish-brown to mahogany color. Their bodies are oval-shaped and measure about 4-5 millimeters in length, roughly the size of an apple seed. When unfed, they appear flattened, but after feeding, they become more elongated and engorged.
Bedbugs have specialized mouthparts that are adapted for piercing skin and sucking blood. They possess a beak-like structure called a proboscis, which they use to pierce the skin and extract blood during feeding.
Life Cycle of a Bed Bug
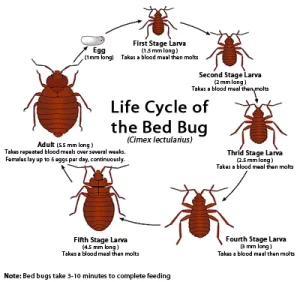
- Egg → First Nymph Instar → Second Nymph Instar → Third Nymph Instar → Fourth Nymph Instar → Fifth Nymph Instar → Adult Bed Bug
Bed bugs require a blood meal to molt and progress through each nymphal stage. The entire life cycle from egg to adult typically takes about 5-8 weeks, but this duration can vary based on factors like temperature, humidity, and food availability. Warm temperatures and ample food can accelerate the bed bug life cycle.
It’s important to note that bed bugs can reproduce rapidly, making it critical to address infestations promptly and thoroughly to prevent a growing population and a more challenging infestation to manage. Professional pest control services are often necessary for effective bed bug elimination.
Where Can Bed Bugs Live?
Bedbugs are attracted to warmth, carbon dioxide, and specific chemicals emitted by their hosts. They are highly adaptable pests that can live in various environments as long as they have access to a blood meal. They typically reside in and around areas where people sleep, hence the name “bedbugs.” However, they can also be found in other areas, such as cracks in furniture, walls, and flooring.
- Homes and Apartments:
- Beds and Mattresses: Seams, folds, crevices, and tufts of mattresses and box springs.
- Furniture: Couches, chairs, and other upholstered furniture with seams and crevices.
- Carpets and Rugs: Edges, folds, and underneath carpets or rugs.
- Closets and Drawers: Especially if they contain clothing or bedding.
- Cracks and Crevices: In walls, flooring, baseboards, and other hiding spots.
- Hotels and Lodging:
- Beds and Bedding: Mattresses, box springs, and bedding in hotel rooms.
- Furniture: Chairs, sofas, and other upholstered furniture.
- Luggage and Bags: Bedbugs can hitch a ride in luggage and bags, potentially infesting new locations.
- Transportation:
- Trains, Buses, and Airplanes: Seats, cushions, and upholstery in public transportation.
- Taxis and Ride-Sharing Vehicles: Seats and upholstery in shared vehicles.
- Public Spaces:
- Theaters and Cinemas: Seats, especially in theaters with fabric upholstery.
- Libraries and Waiting Areas: Chairs and seating in public areas.
- Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities: Beds, waiting room seating, and patient rooms.
- Schools and Educational Institutions:
- Student Housing: Dormitories, beds, and common areas.
- Classrooms and Libraries: Chairs, desks, and seating.
- Laundromats and Clothing Stores:
- Clothing Racks and Displays: Bedbugs can hide in clothing and transfer to homes.
- Workplaces:
- Office Buildings: Seating, waiting areas, and employee workstations.
- Multi-Unit Housing:
- Apartments and Condominiums: Bedbugs can easily spread between units through walls, shared spaces, or shared furniture.
- Vacation Rentals:
- Vacation Homes and Rentals: Bedbugs can be inadvertently carried in by previous guests.
Facts About Bed Bugs

Certainly! Here are some fast facts about bedbugs:
Scientific Name: Bedbugs are scientifically known as Cimex lectularius.
Diet: Bedbugs feed exclusively on the blood of humans and animals. They are obligate blood-feeding ectoparasites.
Size: Adult bedbugs are typically about 4-5 millimeters (mm) in length, roughly the size of an apple seed.
Nocturnal Feeders: Bedbugs are primarily nocturnal, preferring to feed at night when their hosts are asleep. However, they can feed during the day if hungry.
Reproduction: Female bedbugs can lay hundreds of eggs in their lifetime. Eggs are about the size of a pinhead and are laid in cracks, crevices, and other hidden areas.
Life Cycle: Bedbugs undergo an incomplete metamorphosis, with stages including eggs, nymphs (five instars), and adults. Each nymph stage requires a blood meal to molt into the next stage.
Hiding Spots: Bedbugs hide in cracks, crevices, seams, and folds of mattresses, box springs, furniture, and other hiding spots near their hosts.
Travelers’ Pests: Bedbugs can easily hitchhike and spread through travel, infesting hotels, hostels, airplanes, trains, buses, and luggage.
Pesticide Resistance: Bedbugs have developed resistance to many commonly used insecticides, making them challenging to control.
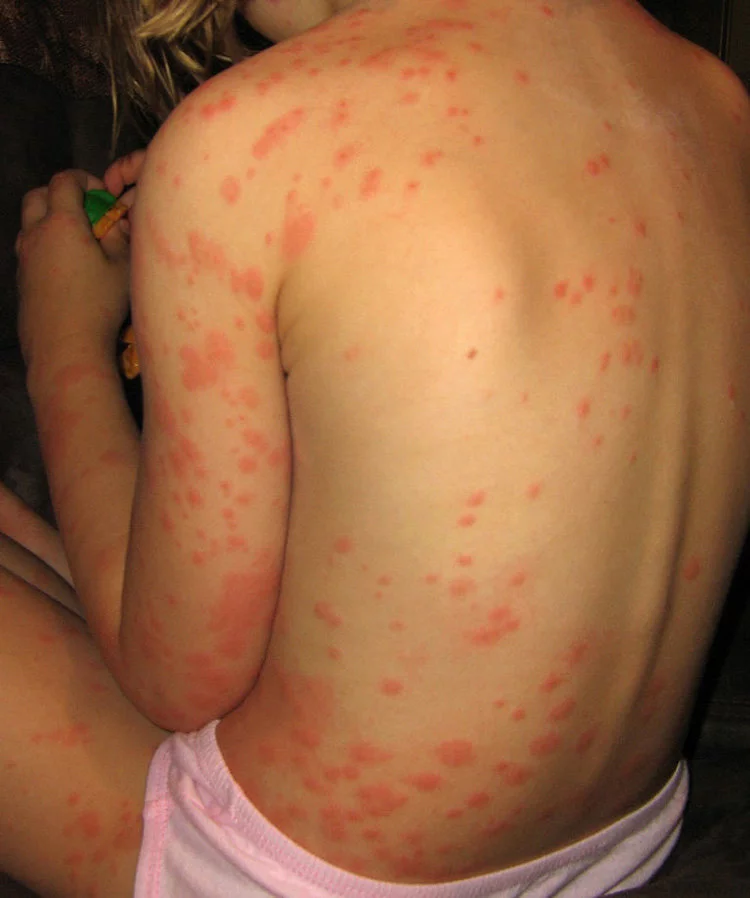
Allergies and Irritation: Bedbug bites can cause skin irritation, redness, itching, and in some individuals, allergic reactions.
Historical Pests: Bedbugs have coexisted with humans for thousands of years. Historical evidence of bedbug infestations dates back to ancient civilizations.
Global Resurgence: Bedbugs have made a significant resurgence in recent decades due to increased travel, pesticide resistance, and lack of awareness.
Heat Treatments: One effective method for eradicating bedbugs is using heat treatments, which can kill bedbugs and their eggs at various life stages.
Prevention: Preventing bedbug infestations involves regular inspection, proper hygiene, avoiding used furniture without inspection, and being cautious during travel.
Professional Pest Control: Managing bedbug infestations often requires professional pest control services to effectively eradicate these pests and prevent reinfestation.
Understanding these fast facts can help individuals be more informed about bedbugs, their behavior, and effective strategies to prevent and manage infestations.
Common Habitats for Bedbugs Include:
- Beds and Mattresses: Particularly in seams, folds, and crevices of mattresses, box springs, and bed frames.
- Furniture: Cracks, crevices, and folds of sofas, chairs, and other upholstered furniture.
- Carpets and Rugs: Edges, folds, and underneath carpets or rugs.
- Behind Wallpaper: In wall cracks or behind peeling wallpaper.
- Electrical Outlets and Switch Plates: As they provide convenient hiding places.
- Luggage and Bags: Especially if they have been in infested areas.
Where Do Bed Bugs Come From
Bed bugs, like many pests, have evolved to adapt to various environments, and their origins can be traced back to ancient times. While the exact origin remains uncertain, bed bugs have likely coexisted with humans for thousands of years.
They are believed to have originated from caves inhabited by bats and birds. They likely fed on the blood of these animals before transitioning to humans as they started living in close proximity to human settlements. Over centuries, bed bugs have evolved to adapt to human environments and become obligate blood-feeding ectoparasites.
Historical records indicate that bed bugs were present in ancient civilizations such as those in Egypt, Greece, and Rome. They were carried across continents through trade, travel, and exploration, infesting ships, homes, and communities.
What Causes Bedbugs?
Bedbugs are primarily caused by a combination of environmental, behavioral, and biological factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective prevention and management of bedbug infestations. Here’s a detailed look at what causes bedbugs:
- Travel and Movement of People
- Used Furniture and Second-Hand Items
- Shared Living Spaces
- Clutter and Untidiness
- Inadequate Cleaning and Hygiene
- Pesticide Resistance
- Lack of Awareness and Education
- Environmental Factors
How Can Bedbugs Be Harmful to My Health?
Bedbugs are generally considered a nuisance rather than a serious health threat, as they do not transmit diseases. However, they can still have several negative effects on your health and well-being, primarily through the physical and psychological impact of their presence and bites. Here’s how bedbugs can be harmful to your health:
- Skin Irritation and Allergic Reactions
- Secondary Infections
- Sleep Disturbance and Mental Health Impact
- Impact on Emotional Well-being
- Insomnia and Fatigue
- Anemia (in rare cases)
- Asthma and Respiratory Issues (rare)
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Financial Burden
Signs of Bed Bug Infestation
- Bite Marks: Red, itchy bite marks often in a linear or clustered pattern on exposed skin, such as arms, legs, neck, and face.
- Blood Stains: Tiny blood spots on sheets, pillowcases, or mattress covers, resulting from the bed bugs being crushed after feeding.
- Fecal Stains: Dark, rust-colored stains on bedding, mattresses, or nearby furniture, a result of bed bug excrement.
- Musty Odor: A sweet, musty odor that may be noticeable in the infested area.
How to Check for Bed Bugs
Checking for bedbugs requires a thorough inspection of your living space and belongings. Early detection can help prevent a small infestation from becoming a larger problem. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to check for bedbugs:
Inspect Bedding and Mattresses:
- Sheets, Pillowcases, and Bed Skirts: Check for small reddish-brown stains (bedbug excrement) or tiny blood spots.
- Seams and Folds: Look for live bedbugs, eggs, or molted exoskeletons in the seams, folds, and creases of the mattress and box spring.
Examine Furniture:
- Couches, Chairs, and Cushions: Inspect seams, folds, and crevices for bedbugs, their eggs, or excrement.
- Drawers and Joints: Check for signs of bedbugs in the joints, cracks, and drawers of furniture.
Inspect Walls and Flooring:
- Cracks and Crevices: Examine wall cracks, baseboards, electrical outlets, and any small openings where bedbugs could hide.
- Carpet Edges: Check along the edges of carpets and rugs, especially in areas near the bed or seating.
Check Other Personal Items:
- Luggage and Bags: Inspect luggage, bags, and purses for bedbugs, especially after traveling or staying in a new location.
- Clothing and Linens: Look for bedbugs in seams, folds, and pockets of clothing, as well as in linen closets.
Inspect the Bed Frame:
- Screws and Joints: Check the joints, screws, and edges of the bed frame for signs of bedbugs.
Use a Flashlight:
A bright flashlight can help you see into dark corners and crevices where bedbugs may hide.
Look for Bedbug Signs:
- Live Bedbugs: Bedbugs are small, flat, reddish-brown insects. Look for them moving or hiding in seams, folds, or cracks.
- Eggs and Eggshells: Tiny white or pale eggs and empty eggshells are signs of bedbug activity.
- Fecal Stains: Small reddish-brown or black stains on mattresses, sheets, or furniture are bedbug excrement.
- Blood Spots: Small blood spots on bedding may indicate crushed bedbugs after feeding.
Set Bedbug Traps:
Place sticky traps or interceptors under the legs of your bed to monitor and trap bedbugs.
Seek Professional Inspection:
If you suspect an infestation or are unsure, consider hiring a professional pest control company for a thorough inspection.
How to Get Rid of Bed Bugs
Getting rid of bed bugs involves a comprehensive approach that combines thorough cleaning, targeted treatments, and preventive measures to ensure effective eradication and long-term prevention. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you eliminate bedbugs from your living space:
Confirm the Infestation:
- Identify the Signs: Make sure you correctly identify bedbugs through physical signs like bites, blood spots, fecal stains, molted skins, and live bedbugs.
Declutter and Clean:
- Declutter: Remove unnecessary items, reducing potential hiding spots for bedbugs.
- Launder Clothing and Bedding: Wash all bedding, linens, curtains, and clothing in hot water (at least 120°F or 49°C) and dry them on the highest heat setting.
- Vacuum Thoroughly: Vacuum mattresses, box springs, bed frames, furniture, carpet edges, and other areas. Dispose of the vacuum bag immediately.
Isolate Infested Items:
- Seal Mattresses and Furniture: Encase mattresses, box springs, and furniture with bedbug-proof covers to trap and isolate bedbugs.
Use Insecticides and Treatments:
- Contact a Pest Control Professional: Consult with a licensed pest control professional to assess the infestation and determine the best treatment plan.
- Insecticidal Sprays: Use insecticides specifically labeled for bedbugs. Follow the instructions carefully and focus on areas where bedbugs hide, such as seams, folds, and crevices.
- Diatomaceous Earth (DE): Apply food-grade DE in cracks, crevices, and hiding spots. DE is a natural insecticide that damages the exoskeleton of bedbugs, leading to dehydration and death.
- Steam Cleaning: Use a high-temperature steam cleaner to treat mattresses, furniture, and other infested areas. Steam effectively kills bedbugs and their eggs.
Heat Treatments:
- Professional Heat Treatment: Consider hiring a professional pest control service that specializes in heat treatments. Heat treatment involves raising the temperature in the infested area to a level that kills bedbugs and their eggs.
Monitor and Follow Up:
- Continued Vigilance: Monitor your living space regularly for signs of bedbugs, even after treatment. If necessary, repeat treatments or contact a professional for follow-up.
Seek Professional Help:
- Pest Control Services: If the infestation is severe or persistent, consider hiring a licensed pest control company specializing in bedbug eradication.
Important Notes:
- Safety: Always follow safety precautions and instructions when using insecticides or treatments.
- Patience and Persistence: Bedbug eradication may take time and repeated efforts. Stay patient and persistent throughout the process.
Remember, effective bed bug control often requires professional assistance to ensure thorough treatment and successful elimination of bedbugs.
Prevention Tips
Preventing a bed bug infestation is essential to maintaining a clean and healthy living space. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
- Regular Cleaning: Vacuum your home regularly, paying close attention to cracks, crevices, and seams where bed bugs can hide.
- Inspect Second-hand Furniture: Before bringing in any used furniture or clothing, carefully inspect for signs of bed bugs.
- Encase Mattresses and Pillows: Use bed bug-proof mattress and pillow covers to minimize the risk of infestation.
- Declutter Your Home: Reduce clutter to eliminate potential hiding spots for bed bugs.
- Be Cautious During Travel: Inspect hotel rooms for signs of bed bugs before unpacking. Keep luggage elevated and away from beds and furniture.
Professional Pest Control
If you suspect a bed bug infestation, seeking professional pest control services is crucial. Professionals can thoroughly inspect your home, identify the extent of the infestation, and implement effective treatments to eliminate bed bugs.
In conclusion, being proactive in preventing bed bug infestations and promptly addressing any signs of an infestation is essential for a pest-free living environment. If faced with a bed bug problem, consider consulting with a pest control expert to ensure thorough eradication and a comfortable, bug-free home.